The following restore functions are provided by CDP:
- List databases in Recovery Point.
- Restore one, several, or all databases.
- Database restore to original or alternate database name/path. See also: MS SQL Server Restore to Alternate Location and MS SQL Server Restore with Alternate Name.
| Tip As an alternative to using the Databases Add-on, you can restore a database's MDF and LDF files using the File Restore function, and then issuing an "Attach Database" query. |
You can restore an MS SQL Server database(s) by following the instructions described below in your CDP Enterprise or Advanced Edition.
1. Click on "Recovery Points" in the Main Menu to open the "Recovery Points" screen.
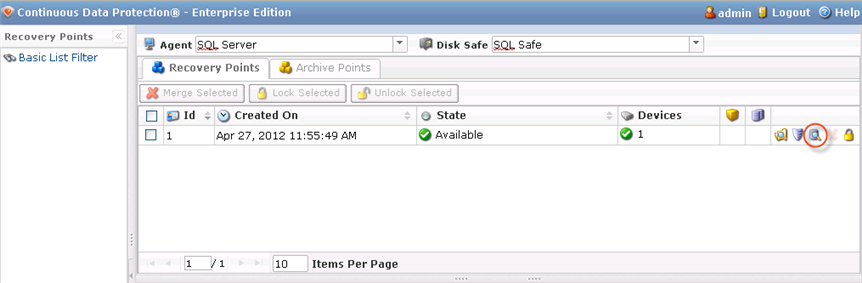
2. In the "Recovery Points" list, select a Recovery Point containing the necessary database replication.
| Tip To find a Recovery Point, you can use the Basic or Advanced List Filter. See Customizing the Recovery Points List. |
Click on the "Browse Databases" icon in the "Actions" column for this Recovery Point.
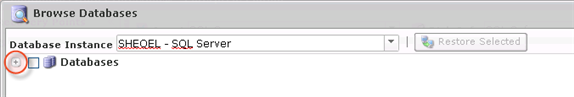
3. The "Browse Databases" window opens. Select a database instance from the drop-down menu.
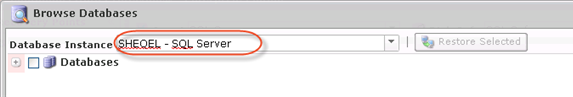
4. You can browse the instance by clicking the "+" icon.
5. Select the database you want to restore and click "Restore Selected."
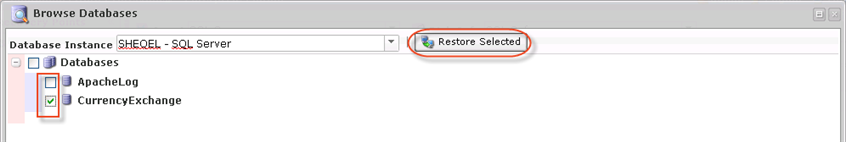
| Notice The system databases master, msdb, model, and tempdb are not displayed in the "Restore Databases" wizard. To restore these databases, use the Bare-Metal Restore function. |
| Tip To be able to restore to an alternate database, do not check the "Databases" box. Instead, select the required databases by clicking the check-box next to each database you want to restore. See also: MS SQL Server Restore with Alternate Name. |
6. In the displayed "Restore Databases" wizard window, define the options for the restore.
When restoring SQL Server databases, you have two options for selecting the host to restore to:
- Restore to Original Host - Restoring to the original host will connect to the host name and the port configured when the Recovery Point was created.
- Restore to Alternate Agent - Restoring to an alternate Agent will connect to the selected Agent's host name and the specified port. Available only in Enterprise Edition. Available only in Enterprise Edition. See Restoring a MS SQL Server to an Alternate Location.
In our example, we selected the "Restore to Original Host" option.
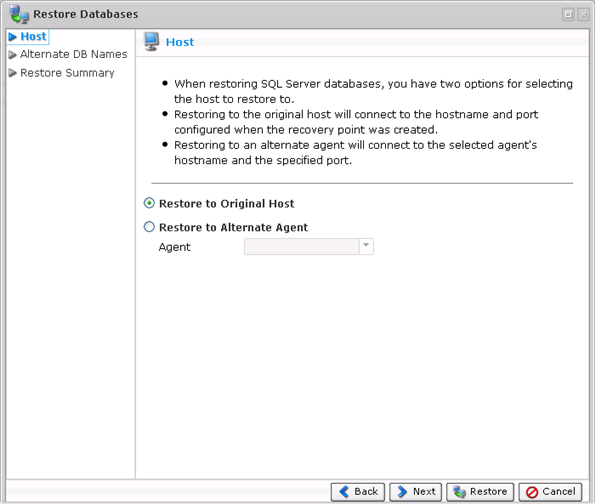
Select an option and click "Next" to proceed to the following step.

7. On the "Alternate DB Names" screen, you may optionally define an alternate database name for any of the selected databases for restore as a new step in the DB restore wizard. If a DB with the new name already exists, that DB restore will fail and will alert the policy.
Expand details to select alternate database paths.
The database can be restored to a different location with a different name. If you want to restore to an alternate location, make sure that you provide the alternate database name and the alternate .mdf and .ldf file paths.
| Tip Do not provide extensions. |
| Tip When performing an MS SQL Server restore to an alternate directory, the directory must already exist. Create an alternate restore directory before restoring the MS SQL Server to it. Read more in MS SQL Server Restore to Alternate Location. |
If you want to restore to the original location, do not provide any of the above information.
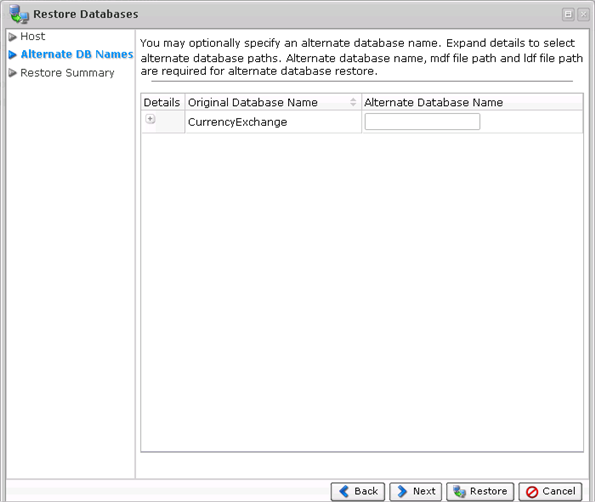
Click "Next" to proceed to the following step.

8. On the last "Summary" screen, the settings you have selected are listed.
9. Once you have verified that the specified settings are correct, click "Restore." The restore process will start immediately.

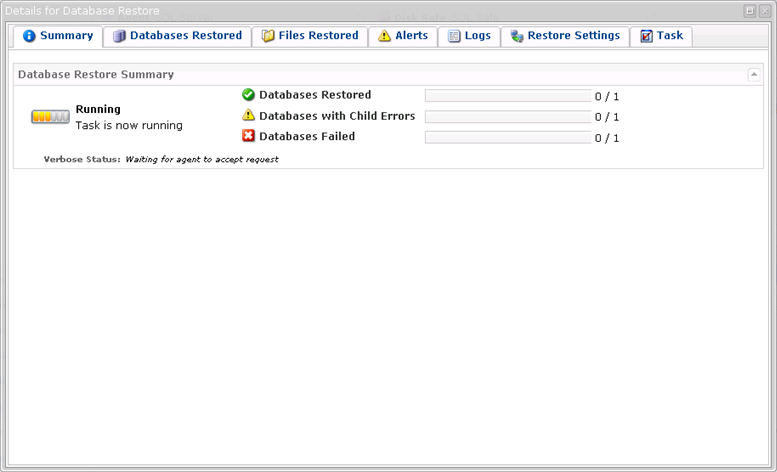
10. The "Details for Database Restore" window will appear. It indicates that the restore process has been launched. You can watch the progress in real time.